Lymphatic System and Immune Response Review Sheet Answers
1
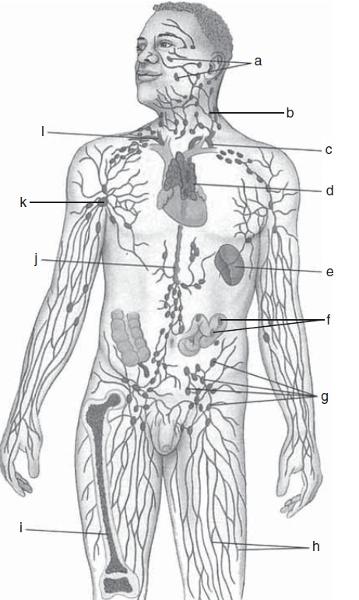
Match the terms with the correct letters in the diagram.
A. TONSILS
B. CERVICAL LYMPH NODES
C. THORACIC DUCT
D. THYMUS
Due east. SPLEEN
F. PEYER'Due south PATCHES (IN INTESTINE)
One thousand. INGUINAL LYMPH NODES
H. LYMPHATIC VESSELS
I. BONE MARROW
J. CISTERNA CHYLI
K. AXILLARY LYMPH NODES
L. RIGHT LYMPHATIC DUCT
2
Explain why the lymphatic system is a one-fashion system, whereas the blood vascular system is a two-fashion system.
Blood vessels form a complete excursion from and to the heart. The lymphatic system lacks arteries and begins with bullheaded-ended lymph capillaries. Thus, it is a "return" system but.
3
How practise lymphatic vessels resemble veins?
The lymphatic collecting vessels accept three tunics and are equipped with valves.
iv
How practice lymphatic capillaries differ from claret capillaries?
Blood capillaries conduct blood from small arterioles to small venules.
Lymphatic capillaries bear lymphatic fluid from tissue to lymphatic venules.
In structure, lymph capillaries are slightly bigger in diameter but have thinner walls than claret capillaries
5
What is the function of the lymphatic vessels?
Lymphatic vessels deport lymph from peripheral tissues to the venous system. The lymphatic system transports lymphocytes, is involved in the removal of strange matter & cell debris by phagocytes & is part of the body'southward immune system. Information technology too transports fats from the small intestine to the claret.
Lymph is a clear to yellowish watery fluid which is found throughout the trunk. It circulates through body tissues picking upwardly fats, bacteria, and other unwanted materials, filtering these substances out through the lymphatic system; a thin coagulable fluid (similar to plasma but) containing white claret cells (lymphocytes) and chyle
7
What factors are involved in the flow of lymphatic fluid?
The milking action of the skeletal muscles and on pressure changes within the thorax that occur during breathing.
8
What name is given to the terminal duct draining nearly of the trunk?
Enlarged terminus of the thoracic duct that receives lymph from the digestive viscera.
x
How does the composition of lymph in the cisterna chyli differ from that in the general lymphatic stream?
They are the same except that the lymph in the cisterna chyli is very fatty-rich
xi
Which portion of the body is tuckered by the right lymphatic duct?
correct upper extremity, head and thorax
12
Note three areas where lymph nodes are densely amassed: _____________, ______________, and ______________.
inguinal, axillary, and cervical regions of the body.
13
What are the two major functions of the lymph nodes? _________________________________ and _______________________________.
14
The radical mastectomy is an operation in which a cancerous breast, surrounding tissues, and the underlying muscles of the anterior thoracic wall, plus the axillary lymph nodes, are removed. Afterwards such an performance, the arm commonly swells, or becomes edematous, and is very uncomfortable -- sometimes for months. Why?
The lymphatic fluid is non being drained from the expanse due to a disruption of lymphatic vessels and nodes.
fifteen
What is the function of B cells in the immune response?
B cells differentiate into plasma cells that secrete antibodies. Antibodies are proteins that bind to specific antigens and mark them for destruction. They provide humoral immunity.
16
What is the role of T cells?
directly set on virus-infected tissue cells, some assist activate the B cells and cytotoxic T cells, and others can inhibit the allowed response. They provide cellular immunity.
17
Ascertain the following term related to the performance of the allowed system.
Immunological memory
when the immunity organisation has/stores a memory from a previously encountered foreign antibody.
18
Ascertain the post-obit term related to the operation of the immune organization.
specificity
the quality of having a certain action, reacting only with certain substances, as antibodies with certain antigens (antigen specificity). Like B cells with antibodies.
19
Define the following term related to the functioning of the immune organization.
recognition of self from nonself
Self recognition immunity is when something goes into the trunk and information technology has been in that location earlier. The body automatically puts a marker specific to only that substance on information technology and so that anytime it is in contact with the body it will recognize it. Not-recognized immunity is when a foreign substance enters the body. In this case the trunk has defense teams designed to assault and rid the torso of the foreign substance.
20
Ascertain the following term related to the operation of the immune organization.
autoimmune disease
When the immune arrangement attacks the body (doesn't recognize a body tissue, identifies it as foreign)
21
What structural characteristic ensures a dull period of lymph through a lymph node? Why is this desirable?
each lymph node has fewer efferent than afferent vessels, so the lymph flow stagnates somewhat inside the node; this is desirable because it allows time for the generation of an immune response and for the macrophages to remove debris from the lymph before it reenters the claret vascular system
22
What similarities in structure and role are found in the lymph nodes, spleen, and tonsils?
Structurally:
o They all have a capsule
o They are rounded organs with an internal parenchyma of lymphoid cells
o They are placed strategically about the body in order to maximally filter air/blood/lymph - meet functional similarities
Functionally:
o All of these organs are involved in the immune organization
o Their role is to filter air/blood/lymph and expose the white blood cells within them to strange material and thus activate the body'south allowed system
23
Distinguish between antigen and antibody.
Antigens are substances that provoke an immune response (they're the ultimate target for the immune organisation). Antibodies are only proteins that are secreted as a effect of the antigen provoked immune response. In short, antigens cause the disease and antibodies cure it.
24
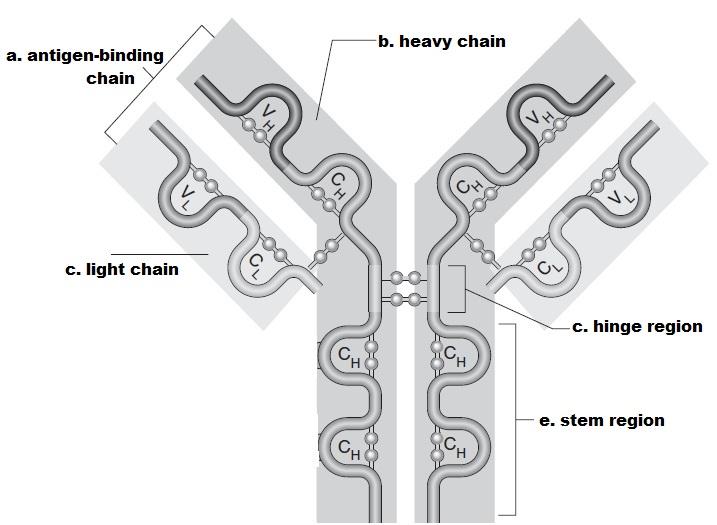
Describe the construction of the immunoglobulin monomer.
Each monomer is composed of four poly peptide chains(2 heavy chains and two lite chains) connected by disulfide bonds. both the heavy and light chains have regions of constnt amino acid sequence (c regions) and regions of variable amino acrid sequence (v regions). The variable regions differ in each type of antibody and construct the antigen-binding sites. Each immunoglobulin monomer has 2 such antigen-specific sites.
25
26
Are the genes coding for one antibody entirely different from those coding for a different antibiotic? Explicate your respond.
no, not entirely. Each antibody (Immunoglobulin, "Ig") has both 2 abiding regions referred to as "heavy hains" and 2 variable regions referred to as "light chains". The structure of the heavy chains remain the same between the unlike antibiotic structures. However, the light chains differ in construction enabling them to respond differently to unlike specific antigens introduced to the cellular membrane.
27
In the Ouchterlony test, what happened when the antibiotic to equus caballus serum albumin mixed with horse serum anbumin?
You will become an antibiotic-antigen reaction. If on a solid phase, like an Ouchterlony agarose gel you lot will see a white precipitin line. If in a liquid, like in a test tube, you lot will see a white precipitate.
28
If the unknown antigen independent bovine and swine serum albumin, what would y'all look to happen in the Ouchterlony examination, and why?
Source: https://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/2313
Post a Comment for "Lymphatic System and Immune Response Review Sheet Answers"